High Availability Deployment
StackStorm has been systematically built with High availability(HA) as a goal. The exact deployment steps to achieve HA depend on the specifics of the infrastructure in which StackStorm is deployed. This guide covers a brief explanation on various StackStorm services, how they interact and the external services necessary for StackStorm to function. Note that StackStorm components also scale horizontally thus increasing the system throughput while achieving higher availability.
In the section Overview: Single-box Reference Deployment a detailed picture and explanation of how single-box deployments work is provided. Let’s reproduce the picture here, to keep some context, and use it as a reference to layer on some HA deployment-specific details.
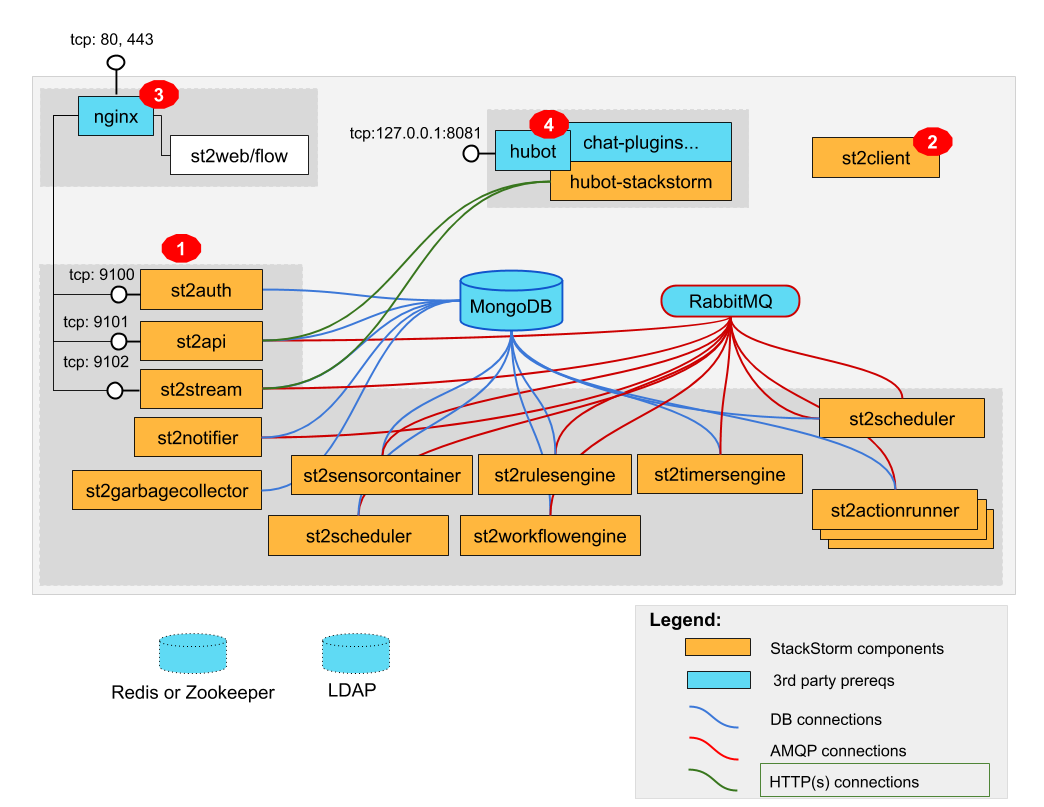
Note
A reproducible blueprint of StackStorm HA cluster is available as a helm chart, which is based on Docker and Kubernetes. See StackStorm HA Cluster in Kubernetes - BETA.
Components
First, a review of StackStorm components:
st2api
This process hosts the REST API endpoints that serve requests from WebUI, CLI and ChatOps. It
maintains connections to MongoDB to store and retrieve information. It also connects to RabbitMQ
to push messages onto the message bus. It is a Python WSGI app running under a gunicorn-managed
process which by default listens on port 9101. It is front-ended by Nginx, acting as a reverse
proxy.
Multiple st2api processes can be behind a load balancer in an active-active configuration.
Each of these processes can be deployed on separate compute instances.
st2auth
All authentication is managed by this process. This process needs a connection to MongoDB and an
authentication backend. See authentication backends for more
information. It is a Python WSGI app running under a gunicorn-managed process which by default
listens on port 9100. It is front-ended by Nginx acting as a reverse proxy.
Multiple st2auth processes can be behind a load balancer in an active-active configuration.
Each of these processes can be deployed on separate compute instances. If using the PAM
authentication backend, special care has to be taken to guarantee that all boxes on which an
instance of st2auth runs should have the same users. Generally, all st2auth process should
see the same identities, via some provider if applicable, for the system to work predictably.
st2stream
This process exposes a server-sent event stream. It requires access to both MongoDB and RabbitMQ.
It is also a gunicorn-managed process, listening on port 9102 by default. It is front-ended by
Nginx acting as a reverse proxy. Clients like WebUI and ChatOps maintain a persistent connection
with an st2stream process and receive update from the st2stream server.
Multiple st2stream process can be behind a load balancer in an active-active configuration.
Since clients maintain a persistent connection with a specific instance the client will briefly
lose events if an st2stream process goes down. It is the responsibility of the client to
reconnect to an alternate stream connection via the load balancer. Note that this is in contrast
with st2api where each connection from a client is short-lived. Take the long-lived nature of
connections made to this process when configuring appropriate timeouts for load balancers, wsgi
app servers like gunicorn etc.
st2sensorcontainer
st2sensorcontainer manages the sensors to be run on a node. It will start, stop and restart
sensors running on a node. In this case a node is the same as a compute instance i.e. a Virtual
Machine. In future this could be a container.
It is possible to run st2sensorcontainer in HA mode by running one process on each compute
instance. Each sensor node needs to be provided with proper partition information to share work
with other sensor nodes so that the same sensor does not run on different nodes.
See Partitioning Sensors for information on how to partition sensors. Currently
st2sensorcontainer processes do not form a cluster and distribute work or take over
new work if some nodes in the cluster disappear. It is possible for a sensor itself to be
implemented with HA in mind so that the same sensor can be deployed on multiple nodes with the
sensor managing active-active or active-passive. Providing some platform level HA support for
sensors is likely to be an enhancement to StackStorm in future releases.
By default sensor container service runs in managed mode. This means that the sensor container process manages child processes for all the running sensors and restarts them if they crash or similar.
In some scenarios this is not desired and service / process life-cycle (restarting, scaling out, etc.) is handled by a third party service such as Kubernetes.
To account for such deployments, sensor container can be started in single sensor mode using
--single-sensor-mode and --sensor-ref command line options. When those options are
provided, sensor container service will run a single sensor and exit immediately if a sensor
crashes or similar.
For example:
st2sensorcontainer --single-sensor-mode --sensor-ref linux.FileWatchSensor
st2rulesengine
st2rulesengine evaluates rules when it sees
TriggerInstances and decide if an ActionExecution is to be requested. It needs access to MongoDB to
locate rules and RabbitMQ to listen for TriggerInstances and request ActionExecutions.
Multiple st2rulesengine processes can run in active-active with only connections to MongoDB and
RabbitMQ. All these will share the TriggerInstance load and naturally pick up more work if one or
more of the processes becomes unavailable.
st2timersengine
st2timersengine is responsible for scheduling all user specified timers. See
timers for the specifics on setting up timers via rules.
st2timersengine process needs access to both Mongo database and RabbitMQ message bus.
You have to have exactly one active st2timersengine process running to schedule all timers.
Having more than one active st2timersengine will result in duplicate timer events and therefore
duplicate rule evaluations leading to duplicate workflows or actions.
To address failover in HA deployments, use external monitoring of the st2timersengine process to ensure
one process is running, and to trigger spinning up a new st2timersengine process if it fails.
Losing the st2timersengine will mean no timer events will be injected into StackStorm and therefore
no timer rules would be evaluated.
st2workflowengine
st2workflowengine drives the execution of orquesta workflows. Once the orquesta action runner
passes the workflow execution request to the st2workflowengine, the workflow engine evaluates
the execution graph generated by the workflow definition and identifies the next set of tasks to
run. If the workflow execution is still in a running state and there are tasks identified, the
workflow engine will launch new action executions according to the task spec in the workflow
definition.
When an action execution completed under the context of an orquesta workflow, the
st2workflowengine processes the completion logic and determines if the task is completed. If
the task is completed, the workflow engine then evaluates the criteria for task transition and
identifies the next set of tasks and launch new action executions accordingly. This continues to
happen until there are no more tasks to execute or the workflow execution is in a completed
state.
Multiple st2workflowengine processes can run in active-active with only connections to MongoDB
and RabbitMQ. All the workflow engine processes will share the load and pick up more work if one or
more of the processes become available. However, please note that if one of the workflow engines
goes offline unexpectedly while processing a request, it is possible that the request or the
particular instance of the workflow execution will be in an unexpected state.
st2actionrunner
All ActionExecutions are handled by st2actionrunner. Once an execution is scheduled
st2actionrunner handles the life-cycle of an execution to one of the terminal states.
Multiple st2actionrunner processes can run in active-active with only connections to MongoDB
and RabbitMQ. Work gets naturally distributed across runners via RabbitMQ. Adding more
st2actionrunner processes increases the ability of StackStorm to execute actions.
In a proper distributed setup it is recommended to setup Zookeeper or Redis to provide a distributed co-ordination layer. See Policies. Using the default file-based co-ordination backend will not work as it would in a single box deployment.
To increase the number of workers per st2actionrunner service, refer to the
Configuring Action Runner workers of the config docs.
st2scheduler
st2scheduler is responsible for handling ingress action execution requests.
It takes incoming requests off the bus and queues them for eventual scheduling
with an instance of st2actionrunner.
Multiple instances of st2scheduler can be run at a time. Database
versioning prevents multiple execution requests from being picked up by
different schedulers. Scheduler garbage collection handles executions that might
have failed to be scheduled by a failed st2scheduler instance.
st2notifier
This is a dual purpose process - its main function is to generate st2.core.actiontrigger and
st2.core.notifytrigger based on the completion of ActionExecution. The auxiliary purpose is to
act as a backup scheduler for actions that may not have been scheduled.
Multiple st2notifier processes can run in active-active mode, using connections to RabbitMQ
and MongoDB. For the auxiliary purpose to function in an HA deployment when more than one
st2notifier is running, either Zookeeper or Redis is required to provide co-ordination. It is
also possible to designate a single st2notifier as provider of auxiliary functions by disabling
the scheduler in all but one st2notifiers.
st2garbagecollector
Optional service that cleans up old executions and other operations data based on setup configurations. By default this process does nothing and needs to be setup to perform any work.
By design it is a singleton process. Running multiple instances in active-active will not yield much benefit, but will not do any harm. The ideal configuration is active-passive but StackStorm itself does not provide the ability to run this in active-passive.
Required Dependencies
This section has some HA recommendations for the dependencies required by StackStorm components. This should serve as a guide only. The exact configuration will depend upon the site infrastructure.
MongoDB
StackStorm uses this to cache Actions, Rules and Sensor metadata which already live in the filesystem. All the content should ideally be source-control managed, preferably in a git repository. StackStorm also stores operational data like ActionExecution, TriggerInstance etc. The Key-Value datastore contents are also maintained in MongoDB.
MongoDB supports replica set high-availability, which we recommend to provide safe failover. See here for how to configure StackStorm to connect to MongoDB replica sets.
Loss of connectivity to a MongoDB cluster will cause downtime for StackStorm. However, once a replica
MongoDB is brought back it should be possible to bring StackStorm back to operational state by
simply loading the content (through st2ctl reload --register-all and st2 key load. Easy
access to old ActionExecutions will be lost but all the data of old ActionExecutions will still
be available in audit logs.
RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ is the communication hub for StackStorm to co-ordinate and distribute work. See RabbitMQ documentation to understand HA deployment strategies.
Our recommendation is to mirror all the Queues and Exchanges so that the loss of one server does not affect functionality.
See here for how to configure StackStorm to connect to a RabbitMQ cluster.
Coordination
Support of workflows with concurrent task executions and concurrency policies for action executions rely on a proper co-ordination backend in a distributed deployment to work correctly.
The coordination service can be configured to use different backends such as redis or zookeeper. For the single node installation script, redis is installed and configured by default.
This shows how to run a replicated Zookeeper setup. (Note: Make sure to refer to the documentation in the same version as your running Zookeeper installation, if any.) See this to understand Redis deployments using sentinel.
Nginx and Load Balancing
An load balancer is required to reverse proxy each instance of st2api, st2auth and
st2stream. In the reference setup, Nginx is used for this. This server
terminates SSL connections, shields clients from internal port numbers of various services
and only require ports 80 and 443 to be open on containers.
Often it is best to deploy one set of all these services on a compute instance and share an Nginx server.
There is also a need for a load balancer to frontend all the REST services. This results in an HA deployment for REST services as well as single endpoint for clients. Most deployment infrastructures will already have a load balancer solution which they would prefer to use so we do not provide any specific recommendations.
Reference HA setup
In this section we provide a highly opinionated and therefore prescriptive approach to deploying
StackStorm in HA. This deployment has 3 independent boxes which we categorize as “controller box” and
“blueprint box.” We’ll call these boxes st2-multi-node-cntl, st2-multi-node-1 and
st2-multi-node-2. For the sake of reference we will be using Ubuntu 18.04 as the base OS.
Obviously you can also use RedHat/RockyLinux/CentOS.
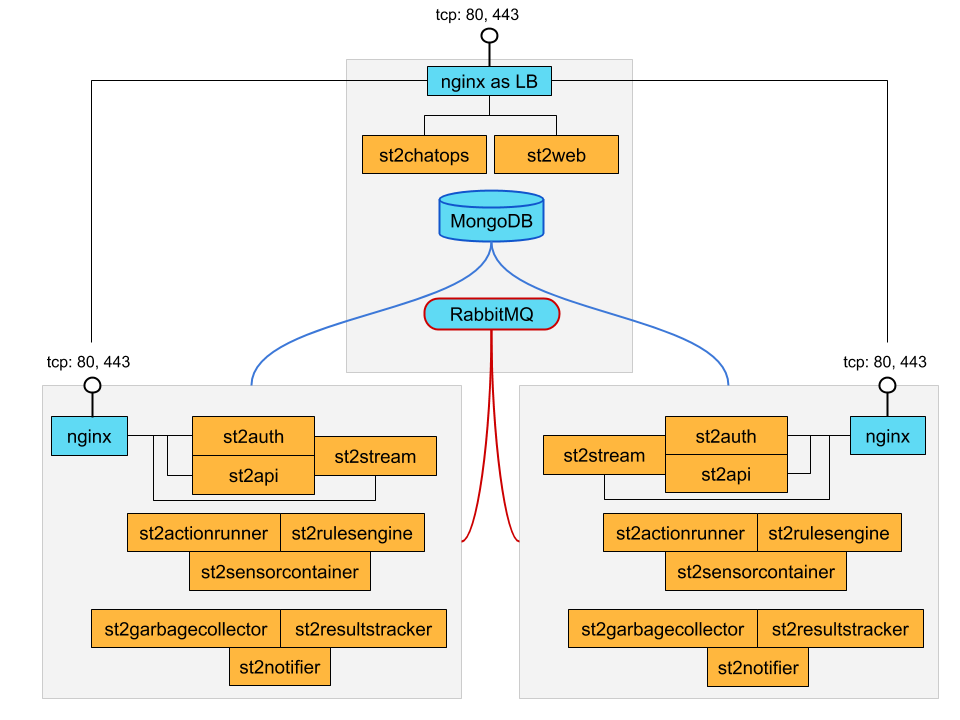
StackStorm HA reference deployment.
Controller Box
This box runs all the shared required dependencies and some StackStorm components:
Nginx as load balancer
MongoDB
RabbitMQ
Redis/Zookeeper
st2chatops
st2web
In practice MongoDB, RabbitMQ, and Redis/Zookeeper will usually be on standalone clusters
managed outside of StackStorm. The two shared components (st2chatops and st2web) are placed here
for the sake of convenience. They could be placed anywhere with the right configuration.
The Nginx load balancer can easily be switched out for Amazon ELB, HAProxy or any other of your
choosing. In that case st2web which is being served off this Nginx instance will also need a
new home.
st2chatops which uses hubot is not easily deployed in HA. Using something like
keepalived to maintain st2chatops in active-passive
configuration is an option.
Follow these steps to provision a controller box on Ubuntu 18.04:
Install Required Dependencies
Install
MongoDB,RabbitMQ, andRedis:The python redis client is already included in the StackStorm virtualenv. If using Zookeeper, the kazoo module needs to be installed into the StackStorm virtualenv.
$ sudo apt-get install -y mongodb-server rabbitmq-server redis-server
Fix
bind_ipin/etc/mongodb.confto bind MongoDB to an interface that has an IP address reachable fromst2-multi-node-1andst2-multi-node-2.Restart MongoDB:
$ sudo service mongodb restart
Add stable StackStorm repos:
$ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/StackStorm/stable/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
Setup
st2weband SSL termination. Follow install webui and setup ssl. You will need to stop after removing the default Nginx config file.A sample configuration for Nginx as load balancer for the controller box is provided below. With this configuration Nginx will load balance all requests between the two blueprint boxes
st2-multi-node-1andst2-multi-node-2. This includes requests tost2apiandst2auth. Nginx also serves as the webserver forst2web.
# # nginx configuration to expose st2 webui, redirect HTTP->HTTPS, # provide SSL termination, and reverse-proxy st2api and st2auth API endpoint. # To enable: # cp ${LOCATION}/st2.conf /etc/nginx/sites-available # ln -l /etc/nginx/sites-available/st2.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/st2.conf # see https://docs.stackstorm.com/install.html for details upstream st2 { server st2-multi-node-1:443; server st2-multi-node-2:443; } server { listen *:80 default_server; add_header Front-End-Https on; add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff; if ($ssl_protocol = "") { return 308 https://$host$request_uri; } index index.html; access_log /var/log/nginx/st2webui.access.log combined; error_log /var/log/nginx/st2webui.error.log; } server { listen *:443 ssl; ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/st2/st2.crt; ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/st2/st2.key; ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m; ssl_session_timeout 5m; ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; ssl_ciphers EECDH+AESGCM:EDH+AESGCM:AES256+EECDH:AES256+EDH:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA128:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA128:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA128:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA128:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA128:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:AES128-GCM-SHA384:AES128-GCM-SHA128:AES128-SHA128:AES128-SHA128:AES128-SHA:AES128-SHA:HIGH:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!MD5:!PSK:!RC4; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; index index.html; access_log /var/log/nginx/ssl-st2webui.access.log combined; error_log /var/log/nginx/ssl-st2webui.error.log; add_header Front-End-Https on; add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff; location @apiError { add_header Content-Type application/json always; return 503 '{ "faultstring": "Nginx is unable to reach st2api. Make sure service is running." }'; } location /api/ { error_page 502 = @apiError; proxy_pass https://st2/api/; proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504; proxy_read_timeout 90; proxy_connect_timeout 90; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header Connection ''; chunked_transfer_encoding off; proxy_buffering off; proxy_cache off; } location @streamError { add_header Content-Type text/event-stream; return 200 "retry: 1000\n\n"; } # For backward compatibility reasons, rewrite requests from "/api/stream" # to "/stream/v1/stream" and "/api/v1/stream" to "/stream/v1/stream" rewrite ^/api/stream/?$ /stream/v1/stream break; rewrite ^/api/(v\d)/stream/?$ /stream/$1/stream break; location /stream/ { error_page 502 = @streamError; proxy_pass https://st2/stream/; proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; # Disable buffering and chunked encoding. # In the stream case we want to receive the whole payload at once, we don't # want multiple chunks. proxy_set_header Connection ''; chunked_transfer_encoding off; proxy_buffering off; proxy_cache off; } location @authError { add_header Content-Type application/json always; return 503 '{ "faultstring": "Nginx is unable to reach st2auth. Make sure service is running." }'; } location /auth/ { error_page 502 = @authError; proxy_pass https://st2/auth/; proxy_next_upstream error timeout http_500 http_502 http_503 http_504; proxy_read_timeout 90; proxy_connect_timeout 90; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-User $remote_user; proxy_pass_header Authorization; proxy_set_header Connection ''; chunked_transfer_encoding off; proxy_buffering off; proxy_cache off; } location / { root /opt/stackstorm/static/webui/; index index.html; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; } }
Create the st2 logs directory and the st2 user:
mkdir -p /var/log/st2 useradd st2
Install
st2chatopsfollowing setup chatops.
Blueprint box
This box is a repeatable StackStorm image that is essentially the single-box reference deployment with a few changes. The aim is to deploy as many of these boxes for desired HA objectives and horizontal scaling. StackStorm processes outlined above can be turned on/off individually, therefore each box can also be made to offer different services.
Add stable StackStorm repos:
$ curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/StackStorm/stable/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
Install all StackStorm components:
$ sudo apt-get install -y st2
Install Nginx:
$ sudo apt-get install -y nginx
Replace
/etc/st2/st2.confwith the samplest2.confprovided below. This config points to the controller node or configuration values ofdatabase,messaging, andcoordination.
# System-wide configuration [api] # Host and port to bind the API server. host = 127.0.0.1 port = 9101 logging = /etc/st2/logging.api.conf mask_secrets = True # allow_origin is required for handling CORS in st2 web UI. # allow_origin = http://myhost1.example.com:3000,http://myhost2.example.com:3000 [stream] logging = /etc/st2/logging.stream.conf [sensorcontainer] logging = /etc/st2/logging.sensorcontainer.conf [rulesengine] logging = /etc/st2/logging.rulesengine.conf [actionrunner] logging = /etc/st2/logging.actionrunner.conf # The line should be commented and 'always-copy' removed when using EL7 or EL8 as it causes virtualenv issues on pack install virtualenv_opts = --always-copy [notifier] logging = /etc/st2/logging.notifier.conf [garbagecollector] logging = /etc/st2/logging.garbagecollector.conf [workflow_engine] logging = /etc/st2/logging.workflowengine.conf [auth] host = 127.0.0.1 port = 9100 use_ssl = False debug = False enable = True logging = /etc/st2/logging.auth.conf mode = standalone # Note: Settings below are only used in "standalone" mode backend = flat_file backend_kwargs = {"file_path": "/etc/st2/htpasswd"} # Base URL to the API endpoint excluding the version (e.g. http://myhost.net:9101/) api_url = [system] base_path = /opt/stackstorm [syslog] host = st2-multi-node-controller port = 514 facility = local7 protocol = udp [log] excludes = requests,paramiko redirect_stderr = False mask_secrets = True [system_user] user = stanley ssh_key_file = /home/stanley/.ssh/stanley_rsa [messaging] url = amqp://guest:guest@st2-multi-node-controller:5672/ [ssh_runner] remote_dir = /tmp use_paramiko_ssh_runner = True [database] host = st2-multi-node-controller [coordination] # url = kazoo://st2-multi-node-controller url = redis://st2-multi-node-controller
Generate a certificate:
$ sudo mkdir -p /etc/ssl/st2 $ sudo openssl req -x509 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/ssl/st2/st2.key -out /etc/ssl/st2/st2.crt \ -days XXX -nodes -subj "/C=US/ST=California/L=Palo Alto/O=StackStorm/OU=Information \ Technology/CN=$(hostname)"
- Configure users & authentication as per this documentation. Make
sure that user configuration on all boxes running
st2authis identical. This ensures consistent authentication from the entire StackStorm install since the request to authenticate a user can be forwarded by the load balancer to any of thest2authprocesses.
- Use the sample Nginx config that is provided below for the blueprint boxes. In this config
Nginx will act as the SSL termination endpoint for all the REST endpoints exposed by
st2apiandst2auth:
# # nginx configuration to expose st2 webui, redirect HTTP->HTTPS, # provide SSL termination, and reverse-proxy st2api and st2auth API endpoint. # To enable: # cp ${LOCATION}/st2.conf /etc/nginx/sites-available # ln -l /etc/nginx/sites-available/st2.conf /etc/nginx/sites-enabled/st2.conf # see https://docs.stackstorm.com/install.html for details server { listen *:80 default_server; add_header Front-End-Https on; add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff; if ($ssl_protocol = "") { return 308 https://$host$request_uri; } index index.html; access_log /var/log/nginx/st2webui.access.log combined; error_log /var/log/nginx/st2webui.error.log; } server { listen *:443 ssl; ssl_certificate /etc/ssl/st2/st2.crt; ssl_certificate_key /etc/ssl/st2/st2.key; ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:10m; ssl_session_timeout 5m; ssl_protocols TLSv1.2 TLSv1.3; ssl_ciphers EECDH+AESGCM:EDH+AESGCM:AES256+EECDH:AES256+EDH:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA128:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA384:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256:DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA128:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA384:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA128:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA128:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA128:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA:AES128-GCM-SHA384:AES128-GCM-SHA128:AES128-SHA128:AES128-SHA128:AES128-SHA:AES128-SHA:HIGH:!aNULL:!eNULL:!EXPORT:!DES:!MD5:!PSK:!RC4; ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on; index index.html; access_log /var/log/nginx/ssl-st2webui.access.log combined; error_log /var/log/nginx/ssl-st2webui.error.log; add_header Front-End-Https on; add_header X-Content-Type-Options nosniff; location /api/ { rewrite ^/api/(.*) /$1 break; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9101/; proxy_read_timeout 90; proxy_connect_timeout 90; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header Connection ''; chunked_transfer_encoding off; proxy_buffering off; proxy_cache off; proxy_set_header Host $host; } # For backward compatibility reasons, rewrite requests from "/api/stream" # to "/stream/v1/stream" and "/api/v1/stream" to "/stream/v1/stream" rewrite ^/api/stream/?$ /stream/v1/stream break; rewrite ^/api/(v\d)/stream/?$ /stream/$1/stream break; location /stream/ { rewrite ^/stream/(.*) /$1 break; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9102/; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; sendfile on; tcp_nopush on; tcp_nodelay on; # Disable buffering and chunked encoding. # In the stream case we want to receive the whole payload at once, we don't # want multiple chunks. proxy_set_header Connection ''; chunked_transfer_encoding off; proxy_buffering off; proxy_cache off; } location /auth/ { rewrite ^/auth/(.*) /$1 break; proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:9100/; proxy_read_timeout 90; proxy_connect_timeout 90; proxy_redirect off; proxy_set_header Host $host; proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for; proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-User $remote_user; proxy_pass_header Authorization; proxy_set_header Connection ''; chunked_transfer_encoding off; proxy_buffering off; proxy_cache off; proxy_set_header Host $host; } }
- To use Timer triggers, enable them on only one server. Make this change in
/etc/st2/st2.conf:[timer] enable = False
- See Partitioning Sensors to decide how to partition sensors to suit your
requirements.
All content should be synced by choosing a suitable strategy as outlined above. This is crucial to obtain predictable outcomes.