StackStorm HA Cluster in Kubernetes - BETA
This document provides an installation blueprint for a Highly Available StackStorm cluster based on Kubernetes, a container orchestration platform at planet scale.
A StackStorm HA cluster consists of 2 replicas for most StackStorm microservices for redundancy and reliability.
The cluster must also have access to backend services like MongoDB HA Replicaset, RabbitMQ HA and a Redis Sentinel cluster
that st2 relies on for database, communication bus, and distributed coordination respectively. These services are
included in the default StackStorm HA cluster, but StackStorm can also use services provisioned separately.
By default, the StackStorm HA cluster consists of a fleet of more than 30 pods.
The source code for K8s resource templates (part of our Helm chart) is available as a GitHub repo: StackStorm/stackstorm-ha.
Warning
Beta quality! This deployment method is in beta. Documentation and code may still be substantially modified and/or refactored.
Requirements
Kubernetes cluster
Helm 3, the K8s package manager (Helm 2 is not supported)
Enough computing resources for production use, respecting System Requirements
Usage
This document assumes some basic knowledge of Kubernetes and Helm. Please refer to K8s and Helm documentation if you find any difficulties using these tools.
However, here are some minimal instructions to get started.
Deployment
The StackStorm HA cluster is available as a Helm chart, a bundled K8s package which makes installing the complex StackStorm infrastructure as easy as:
# Add Helm StackStorm repository
helm repo add stackstorm https://helm.stackstorm.com/
# Install StackStorm HA with an automatically-generated release name in the "default" namespace
# Replace "--generate-name" with a release name if you would like to name the deployment
# Add the "--namespace stackstorm" flag and argument to deploy to the "stackstorm" namespace
# Add "--create-namespace" if the namespace that you are specifying needs to be created
helm install --generate-name stackstorm/stackstorm-ha
Once the deployment is finished, it will show you the first steps to get started with the new cluster via WebUI
or st2 CLI client:
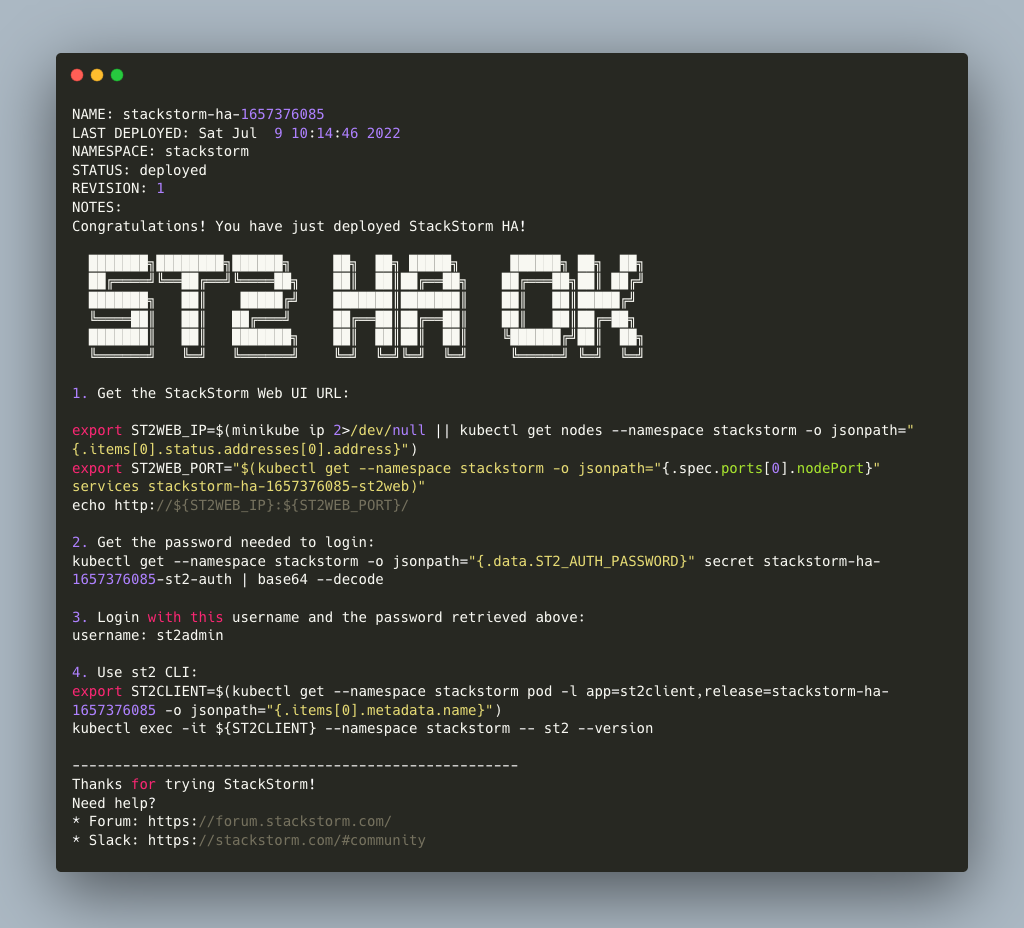
This installation uses unsafe default values. We recommend changing them for production via Helm values.yaml.
Helm Values
Helm package stackstorm-ha comes with default settings (see values.yaml).
Fine-tune them to achieve desired configuration for your StackStorm HA K8s cluster.
Note
Keep custom values you want to override in a separate YAML file so they won’t get lost.
Example: helm install -f custom_values.yaml or helm upgrade -f custom_values.yaml
You can configure:
number of replicas for each component
st2 auth secrets
st2.conf settings
RBAC roles, assignments and mappings (enterprise only for StackStorm v3.2 and before, open source for StackStorm v3.4 and later)
custom st2 packs (in persistent volumes or via custom docker images) and their configs
SSH private key
K8s resources, annotations, and settings to control pod/deployment placement
Image tag and repository settings to select the ST2 version or use customized/private component images
DNS and Ingress configuration
Miscellaneous other ST2 cluster customizations
Mongo, RabbitMQ, and Redis clusters
If not defined, these values are auto-generated on install and preserved across upgrades:
SSH private key
st2 auth secrets (ie: the password for the st2admin user)
Warning
- It’s highly recommended to set your own secrets to replace the unsafe defaults for the MongoDB and RabbitMQ subcharts!
If you disable the subcharts, make sure to secure the services and add the relevant secrets to st2.conf.
Upgrading
After making changes to Helm values, upgrade the cluster:
helm repo update
helm upgrade <release-name> stackstorm/stackstorm-ha
It will redeploy components which were affected by the change, taking care to keep the desired number of replicas to sustain every service alive during the rolling upgrade.
Enterprise (EWC)
For StackStorm versions earlier than 3.3, Extreme Networks provided a commercial version of the StackStorm automation platform (EWC). EWC added priority support, advanced features such as fine-tuned access control (RBAC), LDAP, and Workflow Designer.
As these enterprise features were donated to the Linux Foundation, RBAC, LDAP and Workflow Designer components are now available in StackStorm Open Source since 3.4. The Workflow Designer is integrated into the StackStorm Web UI, and RBAC and LDAP components are installed (but not configured) with the default installation.
Tips & Tricks
Save custom Helm values you want to override in a separate file, upgrade the cluster:
helm upgrade -f custom_values.yaml <release-name> stackstorm/stackstorm-ha
Get all logs for entire StackStorm cluster with dependent services for Helm release:
kubectl logs -l release=<release-name>
Grab all logs only for stackstorm backend services, excluding st2web and DB/MQ/redis:
kubectl logs -l release=<release-name>,tier=backend
Custom st2 packs
There are two ways to install st2 packs in the k8s cluster.
The
st2packsmethod is the default. This method will work for practically all clusters, butst2 pack installdoes not work. The packs are injected viast2packsimages instead.The other method defines shared/writable
volumes. This method allowsst2 pack installto work, but requires a persistent storage backend to be available in the cluster. This chart will not configure a storage backend for you.
Note
In general, we recommend using only one of these methods. See the NOTE under Method 2 below about how both methods can be used together with care.
Method 1: st2packs images (the default)
This method strives to follow the stateless model, so shipping custom st2 packs is part of the deployment process.
Without persistent storage (ie without state), packs and their virtualenvs need to be installed in each pod.
st2 pack install does not work in this distributed model because it assumes that nodes have a shared filesystem
(Method 2, below, uses a shared filesystem), so that only one node needs to download the pack files or setup the
virtualenv and all other nodes will see those files right away.
In order to achieve this stateless model, you have to bundle all the required packs (and their virtualenvs) into one or more Docker images that you can codify, version, package and distribute in a repeatable way. The responsibility of these Docker images is to hold pack content and their virtualenvs. Effectively, the st2packs Docker image(s) you have to build are a couple of read-only directories that are shared with the corresponding st2 services in the cluster. When a new st2actionrunner pod starts up, those directories get copied into the pod.
For your convenience, we created an st2-pack-install <pack1> <pack2> <pack3> utility
and included it in a container stackstorm/st2packs
that will help to install custom packs during the Docker build process without relying on live MongoDB and RabbitMQ connections.
For more detailed instructions see StackStorm/st2packs-dockerfiles on how to build your custom st2packs image.
Please refer to StackStorm/stackstorm-ha#install-custom-st2-packs-in-the-cluster Helm chart repository with more information about how to reference custom st2pack Docker image in Helm values, providing packs configs, using private Docker registry and more.
Ingress
Ingress is worth considering if you want to expose multiple services under the same IP address, and
these services all use the same L7 protocol (typically HTTP). You only pay for one load balancer if
you are using native cloud integration, and because Ingress is “smart”, you can get a lot of
features out of the box (like SSL, Auth, Routing, etc.). See the ingress section in values.yaml
for configuration details.
You will first need to deploy an ingress controller of your preference. See Additional Controllers for more information.
Components
For HA reasons, by default and at a minimum StackStorm K8s cluster deploys more than 30 pods in total.
This section describes their role and deployment specifics.
The Community FOSS Dockerfiles used to generate the docker images for each st2 component are available at StackStorm/st2-dockerfiles.
st2client
A helper container to switch into and run st2 CLI commands against the deployed StackStorm cluster. All resources like credentials, configs, RBAC, packs, keys and secrets are shared with this container.
# obtain st2client pod name
ST2CLIENT=$(kubectl get pod -l app=st2client -o jsonpath="{.items[0].metadata.name}")
# run a single st2 client command
kubectl exec -it ${ST2CLIENT} -- st2 --version
# switch into a container shell and use st2 CLI
kubectl exec -it ${ST2CLIENT} /bin/bash
st2web
st2web is a StackStorm Web UI admin dashboard. By default, st2web K8s config includes a Pod Deployment and a Service.
2 replicas (configurable) of st2web serve the web app and proxy requests to st2auth, st2api, st2stream.
By default, st2web uses HTTP instead of HTTPS. We recommend you rely on LoadBalancer (a Service type) or Ingress to add HTTPS layer on top of it.
Note
By default, st2web is a NodePort Service and is not exposed to the public net. If your Kubernetes cluster setup supports the LoadBalancer service type, you can edit the corresponding helm values to configure st2web as a LoadBalancer service in order to expose it and the services it proxies to the public net.
st2auth
All authentication is managed by the st2auth service.
K8s configuration includes a Pod Deployment backed by 2 replicas by default and Service of type ClusterIP listening on port 9100.
Multiple st2auth processes can be behind a load balancer in an active-active configuration. You can increase the number
of replicas if required.
st2api
This service hosts the REST API endpoints that serve requests from WebUI, CLI, ChatOps and other st2 components.
K8s configuration consists of Pod Deployment with 2 default replicas for HA and ClusterIP Service accepting HTTP requests on port 9101.
This is one of the most important StackStorm services. We recommend increasing the number of replicas to distribute load
if you are planning a high-volume environment.
st2stream
The StackStorm st2stream service exposes a server-sent event stream, used by the clients like WebUI and ChatOps to receive updates from the st2stream server.
Similar to st2auth and st2api, st2stream K8s configuration includes Pod Deployment with 2 replicas for HA (can be increased in values.yaml)
and ClusterIP Service listening on port 9102.
st2rulesengine
st2rulesengine evaluates rules when it sees new triggers and decides if new action execution should be requested.
K8s config includes Pod Deployment with 2 (configurable) replicas by default for HA.
st2timersengine
st2timersengine is responsible for scheduling all user specified timers aka st2 cron. Only a single replica is created via K8s Deployment as timersengine can’t work in active-active mode at the moment (multiple timers will produce duplicated events) and it relies on K8s failover/reschedule capabilities to address cases of process failure.
st2workflowengine
st2workflowengine drives the execution of orquesta workflows and actually schedules actions to run by another component st2actionrunner.
Multiple st2workflowengine processes can run in active-active mode and so minimum 2 K8s Deployment replicas are created by default.
All the workflow engine processes will share the load and pick up more work if one or more of the processes become available.
st2notifier
Multiple st2notifier processes can run in active-active mode, using connections to RabbitMQ and MongoDB and generating triggers based on
action execution completion as well as doing action rescheduling.
In an HA deployment there must be a minimum of 2 replicas of st2notifier running, requiring a coordination backend,
which in our case is redis.
st2sensorcontainer
st2sensorcontainer manages StackStorm sensors: It starts, stops and restarts them as subprocesses.
By default, deployment is configured with 1 replica containing all the sensors.
st2sensorcontainer also supports a more Docker-friendly single-sensor-per-container mode as a way of Partitioning Sensors. This distributes the computing load between many pods and relies on K8s failover/reschedule mechanisms, instead of running everything on a single instance of st2sensorcontainer. The sensor(s) must be deployed as part of the custom packs image.
As an example, override the default Helm values as follows:
st2:
packs:
sensors:
- name: github
ref: githubwebhook.GitHubWebhookSensor
- name: circleci
ref: circle_ci.CircleCIWebhookSensor
st2actionrunner
Stackstorm workers that actually execute actions.
5 replicas for K8s Deployment are configured by default to increase StackStorm ability to execute actions without excessive queuing.
Relies on redis for coordination. The st2actionrunner replicas count is likely the first thing to increase if you have
a lot of actions to execute per time period in your StackStorm cluster.
st2scheduler
st2scheduler is responsible for handling ingress action execution requests.
2 replicas for K8s Deployment are configured by default to increase StackStorm scheduling throughput.
Relies on database versioning for coordination.
st2garbagecollector
Service that cleans up old executions and other operations data based on setup configurations.
Having 1 st2garbagecollector replica for K8s Deployment is enough, considering its periodic execution nature.
By default this process does nothing and needs to be configured in st2.conf settings (via values.yaml).
Purging stale data can significantly improve cluster abilities to perform faster and so it’s recommended to configure st2garbagecollector in production.
st2chatops
StackStorm ChatOps service, based on hubot engine, custom stackstorm integration module and preinstalled list of chat adapters.
Due to Hubot limitation, st2chatops doesn’t provide mechanisms to guarantee high availability and so only single 1 node of st2chatops is deployed.
This service is disabled by default. Please refer to Helm values.yaml about how to enable and configure st2chatops with ENV vars for your preferred chat service.
MongoDB HA ReplicaSet
StackStorm works with MongoDB as a database engine. External Helm Chart is used to configure MongoDB HA ReplicaSet.
By default 3 nodes (1 primary and 2 secondaries) of MongoDB are deployed via K8s StatefulSet.
For more advanced MongoDB configuration, refer to official mongodb-replicaset
Helm chart settings, which might be fine-tuned via values.yaml.
The deployment of MongoDB to the k8s cluster can be disabled by setting the mongodb-ha.enabled key in values.yaml to false.
Note
Stackstorm relies heavily on connections to a MongoDB instance. If the in-cluster deployment of MongoDB is disabled, a connection to an external instance of MongoDB must be configured. The st2.config key in values.yaml provides a way to configure stackstorm. See Configure MongoDB for configuration details.
RabbitMQ HA Cluster
RabbitMQ is a message bus StackStorm relies on for inter-process communication and load distribution.
External Helm Chart is used to deploy RabbitMQ cluster in Highly Available mode.
By default 3 nodes of RabbitMQ are deployed via K8s StatefulSet.
For more advanced RabbitMQ configuration, please refer to official rabbitmq-ha
Helm chart repository, - all settings could be overridden via values.yaml.
The deployment of RabbitMQ to the k8s cluster can be disabled by setting the rabbitmq-ha.enabled key in values.yaml to false.
Note
Stackstorm relies heavily on connections to a RabbitMQ instance. If the in-cluster deployment of RabbitMQ is disabled, a connection to an external instance of RabbitMQ must be configured. The st2.config key in values.yaml provides a way to configure stackstorm. See Configure RabbitMQ for configuration details.
redis
StackStorm employs redis as a distributed coordination backend, required for st2 cluster components to work properly in an HA scenario.
3 node cluster with Sentinel is deployed via external official Helm chart dependency bitnami/redis.
As any other Helm dependency, it’s possible to further configure it for specific scaling needs via values.yaml.
Feedback Needed!
As this deployment method is new and beta is in progress, we ask you to try it and provide your feedback via
bug reports, ideas, feature or pull requests in StackStorm/stackstorm-k8s,
and encourage discussions in Slack #k8s channel.